Generative AI has moved from experimental use cases into production environments where businesses are transforming how they create, deliver, and measure value. It’s now being integrated into everyday operations, particularly where high-frequency decisions intersect with data, language, and customer interactions.
As Principal Product Manager at SAP, I’ve funneled AI-driven opportunities focused on GenAI to build a pipeline of high-impact use cases for project-led organizations. These efforts go beyond pilot projects, resulting in full-scale implementations that improve response times, reduce operational load, and drive revenue by enabling faster, more accurate decisions.
Unlike rule-based automation, GenAI learns from context, processes natural language, and improves with every new input. This makes it ideal for streamlining knowledge-heavy processes across finance, operations, customer support, marketing, and product development.
This article focuses on practical implementations of generative AI, how companies are capturing new revenue opportunities, and the common mistakes that can derail impact.
The Growing Impact of Generative AI on Business Innovation
The rise of generative AI marks a structural shift in enterprise architecture. Organizations are embedding models into language-based workflows, building cross-functional tools for dynamic decision support, and personalizing customer interaction in real time.
McKinsey estimates that the potential economic contribution of generative AI could range between $2.6 trillion and $4.4 trillion annually. That value is most pronounced in functions like marketing, customer operations, R&D, and software engineering, where language is central to workflow and decision-making.

The core distinction lies in how GenAI systems reason. They don’t apply static logic; they infer, suggest, and generate, enabling new ways to interact with both data and customers. But without the right technical planning, integrations, and iteration, these projects can quickly stall. The goal isn’t experimentation. It’s output that moves the business forward.
Use Cases That Drive Measurable Business Value
The following business functions highlight how generative AI is already delivering tangible returns when applied with measurable objectives and strong feedback mechanisms.
1. Customer Support at Scale Using Conversational AI
Support functions are resource-heavy, complex, and frequently under-optimized. Generative AI offers a way to reduce load without degrading service. When fine-tuned on industry-specific dialogue and policies, LLM-based agents can triage, route, and resolve inquiries without relying on decision trees or predefined scripts.
Manulife’s integration of Azure-powered virtual assistants is a prime example. Their AI system handles customer interactions in multiple languages across product lines while improving response time and reducing live agent dependency. These improvements didn’t come from reducing headcount, but by reassigning human support to higher-complexity issues.
The takeaway is that AI support systems must be trained on operational data and governed by feedback loops. When managed properly, they cut cost-per-interaction and enable scalable service across time zones and product lines.
2. Streamlining Operations Through Business Process Automation
In domains like finance, compliance, and supply chain management, repetitive workflows often slow down decision velocity and inflate costs. Generative AI addresses this by automating documentation, report generation, and even complex tasks like interpreting regulatory updates.
One standout implementation comes from Deloitte’s work with SAP, where GenAI was integrated directly into SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP). These solutions now automate code generation and documentation tasks—shrinking project timelines and minimizing manual overhead for enterprise users managing financials and supply chain data.
By combining language understanding with domain-specific workflows, companies are making previously manual cycles faster, cheaper, and more accurate.
3. Democratizing Data Analysis for Non-Technical Teams
Analytics systems often gate insight behind SQL queries, dashboards, or BI tools that require training. GenAI changes this by creating interfaces where business users ask questions and receive clear answers without translation layers.
Organizations can democratize access to information by pairing GenAI with well-curated, query-ready internal data. The biggest returns come when analytics stop being a bottleneck and become a proactive business asset.
For example, Lucy®, built on Azure OpenAI, was designed as an innovative “answer engine®” that lets departments surface relevant trends buried in unstructured documents and data lakes. Marketing, HR, and sales teams can now generate insights and reports without writing SQL or relying on analysts, reducing the turnaround time for data-driven decisions.
“We believe in technology not to replace people, but to enable them to learn things they didn’t know existed, do their jobs better, be more effective, make smarter strategic decisions, and be more informed.”
— Steve Frederickson, Chief Product Officer, Lucy
4. Automating Content Production in Modern Marketing
Content production is central to modern marketing, but the marketing function often struggles with scale: how to generate content that reflects brand voice, adapts to performance data, and targets a diverse audience without inflating cost.
Generative AI has the potential to make the marketing function progressively more sophisticated over time. Companies begin by integrating off-the-shelf tools like ChatGPT to assist with first-draft copy for emails or blog posts. These early-stage applications improve efficiency but rely on general-purpose models.
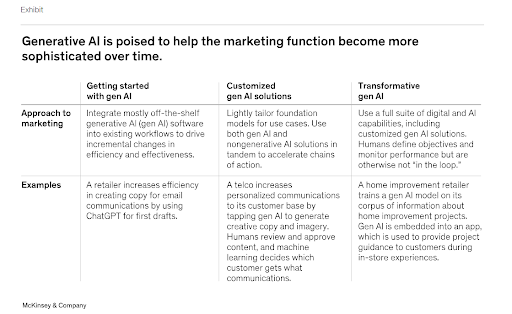
The next wave of value creation comes when organizations customize generative AI solutions by pairing large language models with internal customer data, enabling dynamic personalization. Human teams validate and guide these outputs, but AI now handles the bulk of the creative iteration, accelerating time-to-market.
More advanced organizations are embedding GenAI throughout the entire content lifecycle. Some platforms now analyze audience behavior, suggest formats, and generate full campaigns that drive measurable engagement lift without increasing headcount. This evolution enables marketers to test, iterate, and launch campaigns that are both faster and more precisely aligned with real-time audience behavior.
5. Speeding Product Design and Validation
Consumer product teams utilize generative models to explore designs, validate assumptions, and simulate prototypes pre-production. In the beverage industry, companies enhance product development, especially in flavor creation and testing. For instance, Givaudan leverages AI tools to analyze consumer preferences and predict innovative flavor combinations, creating new profiles before committing to physical prototypes.
By embedding GenAI into the creative and product development pipeline, teams can:
- Generate personalized product concepts based on regional preferences and trends
- Simulate consumer interactions to optimize packaging, formulations, or marketing messages
- Reduce time-to-market by accelerating feedback loops between R&D, marketing, and retail
Generative tools should be used for concept validation, not just visual generation. When AI proposals are run through simulation models and stress tests, product cycles compress while improving confidence in performance, cost, and manufacturability.

Where Projects Go Off Track: Key Considerations for Implementing Generative AI
Even with promising use cases, many deployments stall due to flawed assumptions or weak operational planning. These are the most common—and avoidable—breakpoints:
Expecting Immediate Results
Off-the-shelf LLMs provide generic value but need customization to match industry-specific language and workflows. Deployments that skip orchestration, feedback loops, or fine-tuning underperform and often fail to show ROI.
Misdefining the Role of Generative AI
Generative AI is not a replacement for robotic process automation. It creates new outputs, not just executes logic. Frame it as a creative system that requires supervision, not just a faster back-office tool.
Underinvesting in Feedback and Adaptation
Model outputs degrade over time if not retrained or calibrated with updated data. Implement robust monitoring for accuracy and drift, and close the loop with human feedback for continuous improvement.
Overlooking Culture and Governance
Success depends as much on team dynamics as on technical execution. AI literacy, collaboration between technical and domain teams, and a shared understanding of AI boundaries are all prerequisites. Set up decision frameworks and performance audits early.
Conclusion: Generative AI as an Integrated Business Component
Generative AI is a transformative force that can redefine business success. It works best when integrated directly into business systems, supporting decision-making, reducing delay, and assisting teams where they work. The outcome isn’t just better performance—it’s the ability to respond faster, test more ideas, and focus human talent where it matters most.
To realize these benefits, organizations must embed generative AI into the systems people use daily. That means prioritizing integration, building in feedback mechanisms, and designing clear governance from day one. GenAI systems should support—not replace—human judgment, and they should evolve alongside business goals.
Business success comes from treating generative AI as part of the operational foundation—tested, measurable, and aligned with real objectives.
About the Author:
Akhil Kumar Pandey is a Principal Product Manager at SAP, leading initiatives that embed generative AI into enterprise cloud platforms like S/4HANA and BTP. With over 15 years of experience spanning product strategy, AI innovation, and enterprise software integration, Akhil brings a practitioner’s insight into the transformative power of GenAI in real-world business contexts.
References:
Chui, M., Hazan, E., Roberts, R., Singla, A., Smaje, K., Sukharevsky, A., Yee, L., & Zemmel, R. (2023, June 14). The economic potential of generative AI: The next productivity frontier. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/mckinsey-digital/our-insights/the-economic-potential-of-generative-ai-the-next-productivity-frontier#business-and-society
John Hancock supports call center teams with Microsoft conversational AI tools. (2023, June 5). Microsoft Customer Stories. https://www.microsoft.com/en/customers/story/1642618423217607453-Manulife-John-Hancock-Insurance-Azure
Deloitte expands SAP® business technology platform with generative AI to deliver services and solutions focused on outcomes and client value. (2023, October 13). Deloitte. https://www.deloitte.com/global/en/about/press-room/deloitte-expands-sap-business-technology-platform-with-generative-ai.html
Lucy® the Answer Engine® broadens her knowledge and scope with Azure. (2023, November 9). Microsoft Customer Stories. https://www.microsoft.com/en/customers/story/1700954751530838723-lucy-azure-united-states
Harkness, L., Robinson, K., Stein, E., & Wu, W. (2023, December 5). How generative AI can boost consumer marketing. McKinsey & Company. https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/growth-marketing-and-sales/our-insights/how-generative-ai-can-boost-consumer-marketing
Aggarwal, M. (2023, May 15). 10 Innovative Ways Gen AI is Transforming the Energy Drink Industry: Unleashing Potential and Boosting Performance with Large Language Models. Pluto7. https://pluto7.com/2023/05/15/ai-in-beverage-industry/
